
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has a pivotal role in assessing brain injury in CO poisoning. 1, 6 To date, no reliable methods of assessing the probability of DNS after acute CO poisoning have been developed.

1 - 5 Neurological symptoms of CO poisoning can manifest not only immediately but also as late as 2 to 6 weeks after successful initial resuscitation as delayed neurological sequelae (DNS).
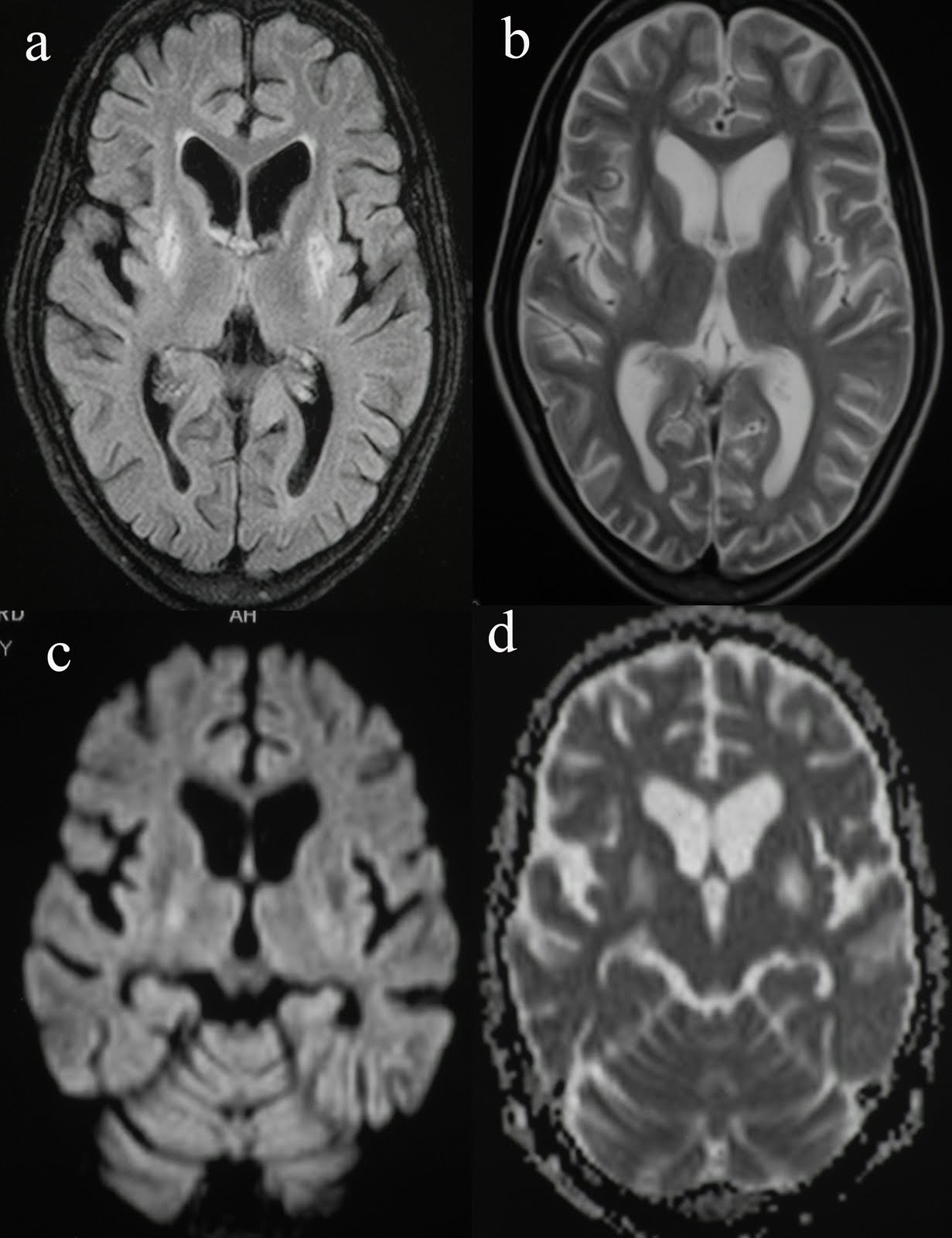
Diffusion-weighted imaging during the acute phase of carbon monoxide poisoning may therefore help identify patients at risk of developing these debilitating sequelae.Ĭarbon monoxide (CO) poisoning, which causes hypoxic insults to the brain and other organs, is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity. In addition, the positive and negative predictive values were 73.1% (95% CI, 64.6%-81.6%) and 91.2% (95% CI, 87.9%-94.5%), respectively.Ĭonclusions and Relevance The presence of acute brain lesions was significantly associated with the development of delayed neurological sequelae. The sensitivity and specificity of acute brain lesions to assess the probability of delayed neurological sequelae were 75.2% (95% CI, 66.8%-83.7%) and 90.2% (95% CI, 86.8%-93.7%), respectively. Multivariable logistic regression analysis indicated that the presence of acute brain lesions was independently associated with development of delayed neurological sequelae (adjusted odds ratio, 13.93 95% CI, 7.16-27.11 P < .001). Delayed neurological sequelae occurred in 101 patients (26.1%). Lesions were supratentorial and infratentorial in 101 and 23 patients, respectively. Among these, 77 patients (19.9%) had globus pallidus lesions, 13 (3.4%) had diffuse lesions, and 57 (14.7%) had focal lesions (37 patients had >1 pattern concurrently). Results Of the 387 included patients (143 women median age, 42.0 years ), acute brain lesions on diffusion-weighted imaging were observed in 104 patients (26.9%). Main Outcomes and Measures Development of delayed neurological sequelae defined as any neurological symptoms or signs that newly developed within 6 weeks of discharge. Patients who developed cardiac arrest before diffusion-weighted imaging (n = 3), had persistent neurological symptoms at discharge (n = 8), committed suicide soon after discharge (n = 1), and were lost to follow-up (n = 34) were excluded.Įxposure The presence of unambiguous, high-signal-intensity, acute brain lesions on diffusion-weighted imaging ( b = 1000 s/mm 2). Of 700 patients (aged ≥18 years) with acute carbon monoxide poisoning, 433 patients (61.9%) who underwent diffusion-weighted imaging at an emergency department were considered for the study. Objectives To determine whether acute brain lesions on diffusion-weighted imaging are related to subsequent development of delayed neurological sequelae after acute carbon monoxide poisoning.ĭesign, Setting, and Participants This registry-based observational study was conducted at a university hospital in Seoul, Korea, between April 1, 2011, and December 31, 2015.

Importance Preventing delayed neurological sequelae is a major goal of treating acute carbon monoxide poisoning, but to our knowledge there are no reliable tools for assessing the probability of these sequelae.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
